FAQ on Foreign Portfolio Flows into Equity Markets
Foreign portfolio flows in and out of a country can impact the performance of a country’s equity market. This FAQ explains the factors that drive foreign portfolio flows and what they mean for investors.

1. What are foreign portfolio flows?
Foreign portfolio flows arise as a result of the purchase and sale of financial assets such as equities by foreign investors in a host country. The main focus of foreign portfolio investment is to seek capital gains or higher yields in the country’s financial markets.
Meanwhile, for the host country, the inflow of foreign funds helps to deepen and enhance the country’s capital markets as it enlarges the pool of opportunities for local companies to access funds. However, foreign portfolio flows can be volatile at times, causing fluctuations in financial markets.
2. How are foreign portfolio flows different from foreign direct investments (FDI)?
Foreign portfolio flows typically involve investments in tradeable financial assets like stocks and bonds. On the other hand, FDI refers to investments by foreign companies in physical fixed assets such as factories and equipment.
FDI is generally seen as a strategic, long-term commitment, while portfolio flows are more liquid and prone to short-term market fluctuations. FDI contributes directly to economic growth by creating jobs and increasing output, while portfolio investments are financial in nature, indirectly contributing to economic benefits.
3. What are some of the factors affecting foreign portfolio flows into a host country’s equity markets?
There are many factors that could impact foreign portfolio flows into a host country’s equity markets, such as:
a. Corporate earnings outlook
The anticipation of better corporate earnings prospects may drive foreign portfolio flows into a country’s capital markets. Investors pay close attention to corporate earnings as stock prices ultimately move in tandem with corporate earnings over the long term.
b. Economic prospects
Foreign portfolio investors tend to be attracted to investing in countries with good long-term economic prospects and supportive government policies.
c. Exchange rates
Portfolio investors also consider the exchange rate outlook of foreign countries. If a country’s currency is expected to strengthen, foreign investors are more likely to invest in its financial assets in order to benefit from the currency’s appreciation.
4. Why has Bursa Malaysia experienced volatile foreign fund flows?
In 2020-2021, Bursa Malaysia registered net foreign portfolio outflows (Figure 1) amid the Covid-19 pandemic. However, net foreign portfolio flows turned positive in 2022 as the lifting of the movement control restrictions led to a recovery in Malaysia’s economic growth and corporate earnings.
Subsequently, in 2023-2024, net foreign portfolio flows were negative amid volatility in the Ringgit due to higher U.S. interest rates. For the year-to-date (YTD) period until 31 July 2025, Bursa Malaysia registered net foreign portfolio outflows amid uncertainties over the economic impact of higher U.S. tariffs on Malaysia’s exports to the U.S.
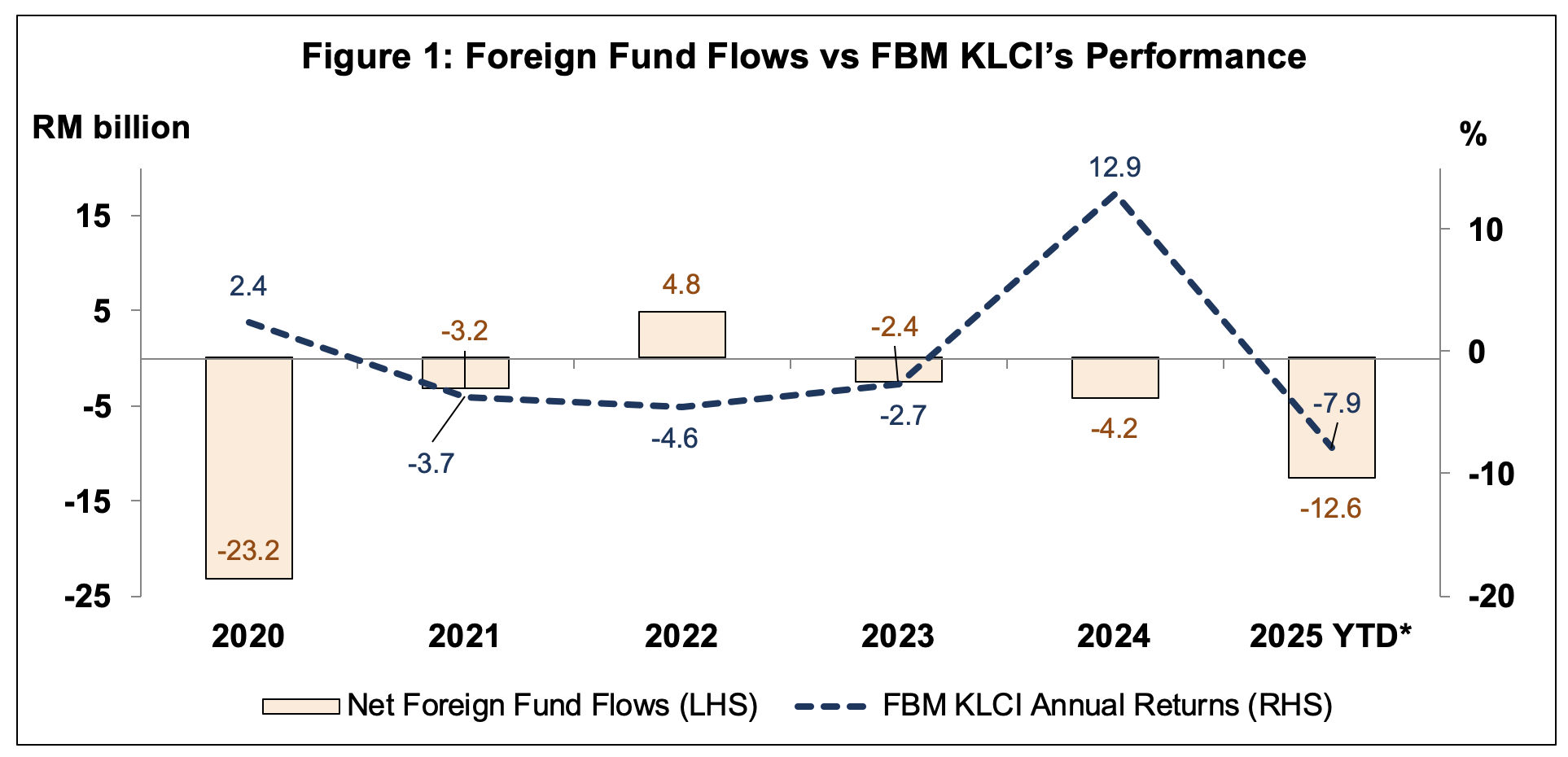 Source: Bloomberg *Year-to-date (YTD) as at 31 July 2025
Source: Bloomberg *Year-to-date (YTD) as at 31 July 2025
In general, foreign portfolio flows into a market may help drive stock prices up, resulting in the strengthening of a country’s stock market indices. On the flip side, when foreign funds flow out of the market, the market indices may face downward pressure.
Despite the net foreign portfolio outflows, participation by local institutional and retail investors may help to mitigate the effect of foreign investors exiting the market.
Conclusion
It is useful for investors to understand the impact and factors affecting foreign portfolio flows and their effect on the stock markets. As foreign portfolio flows into equity markets can be volatile, investors are advised to diversify across different geographical regions in accordance with their risk profiles. Over the longer term, the performance of equity markets is underpinned by their respective corporate earnings prospects and macroeconomic fundamentals.
This article is prepared solely for educational and awareness purposes and should not be construed as an offer or a solicitation of an offer to purchase or subscribe to products offered by Public Mutual. No representation or warranty is made by Public Mutual, nor is there acceptance of any responsibility or liability as to the accuracy, completeness or correctness of the information contained herein.